Table of Contents
Toggle
RFID Definition stands for Radio Frequency Identification , a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects automatically. This technology allows businesses and industries to tag items with small electronic devices that store data and communicate wirelessly with RFID readers. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be retrieved from a distance without requiring physical contact or line-of-sight scanning.
The adoption of RFID Definition is increasing in various sectors such as logistics, healthcare, retail, and security, as it significantly enhances efficiency and automation. Businesses can use it to track inventory in real time , prevent theft, authenticate users, and streamline various operations. The ease of data collection and integration makes RFID Definition a valuable asset for companies looking to modernize their processes.
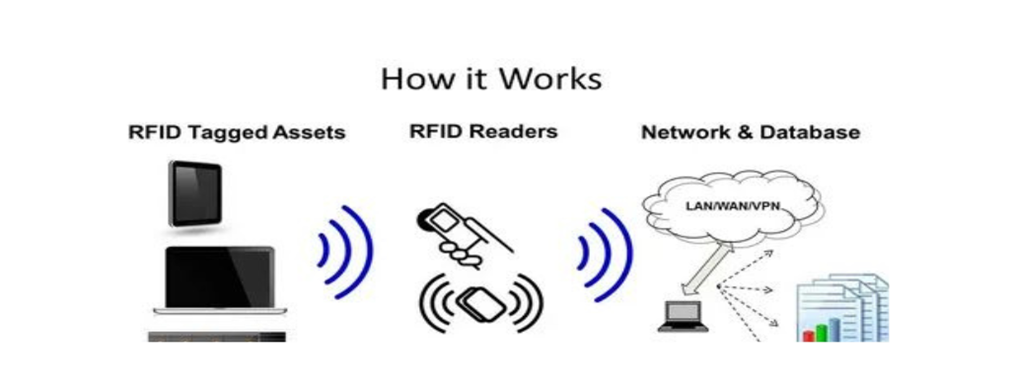
How Does RFID Work?
At its core, RFID Definition operates using radio waves to communicate between an RFID tag and an RFID reader. When the reader emits radio signals, the RFID tag's microchip and antenna receive these signals, allowing the stored data to be transmitted back to the reader. This data is then processed in a central database, where it can be analyzed and used for tracking and monitoring purposes.
The technology enables businesses to track products and assets without human intervention, reducing manual errors and enhancing accuracy. The ability to identify multiple RFID tags simultaneously, even in large storage facilities or warehouses, makes RFID Definition a game-changer for logistics and supply chain management. It is faster, more secure, and more reliable than traditional barcode systems, allowing for seamless automation.
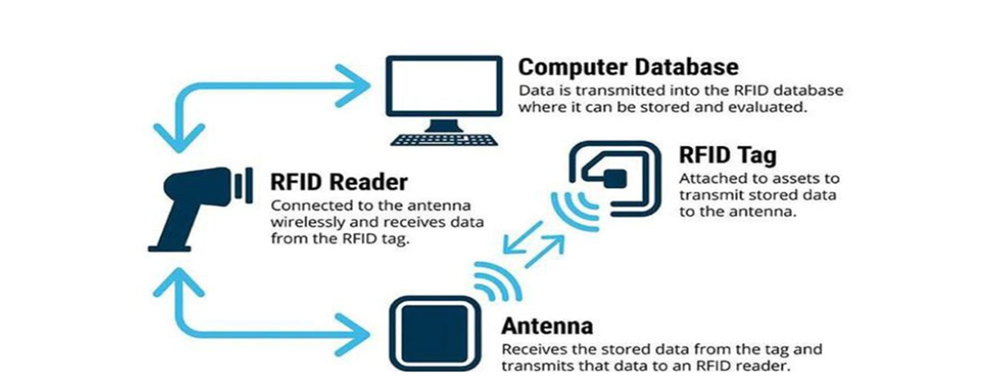
Key Components of an RFID System
- RFID Tags – These tags store unique identification information and come in two types:
- Active Tags – They have an internal battery that powers them and allows long-range communication.
- Passive Tags – They do not have a battery and rely on energy from the RFID reader’s signal.
- RFID Readers – These devices send radio signals to activate the RFID tags and retrieve stored data.
- Antenna – Facilitates communication between RFID tags and readers by transmitting and receiving radio waves.
- Software & Database – Collects, processes, and manages the data from RFID tags, ensuring real-time tracking and reporting.
- Network Infrastructure – Enables connectivity between RFID readers, databases, and analytical tools for seamless integration.
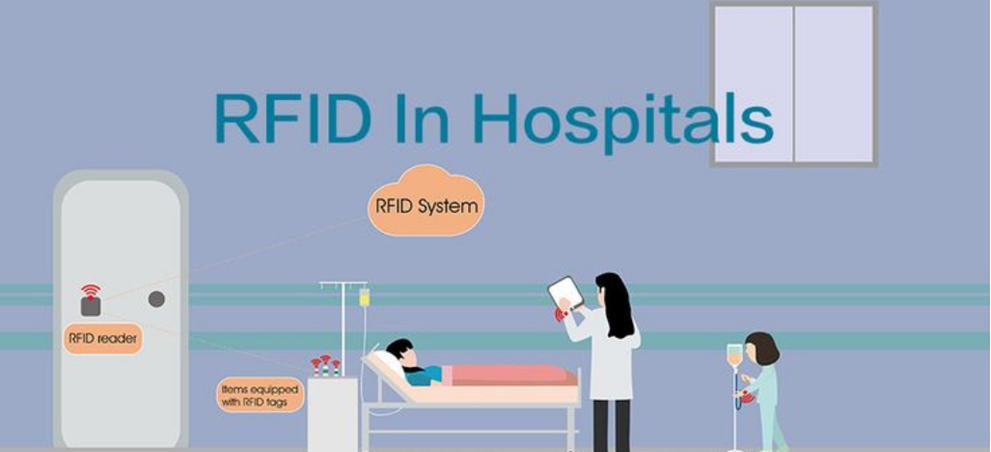
Common Uses of RFID Definition Technology
- Retail & Inventory Management – Retail stores use RFID to track inventory in real time, preventing stock shortages and theft while improving customer service.
- Supply Chain & Logistics – Warehouses and distribution centers rely on RFID to monitor shipments, track goods in transit, and automate inventory counting.
- Healthcare – RFID is used in hospitals to track medical equipment, manage patient records, and ensure medication safety.
- Access Control & Security – Companies use RFID for secure access control in office buildings, airports, and government institutions.
- Automotive & Transportation – RFID is widely implemented in electronic toll collection systems, smart ticketing for public transport, and vehicle tracking.
Key Features of RFID Definition
- The effectiveness of RFID Definition technology stems from its robust features that cater to different business needs. One of its key features is automatic identification and tracking, which provides real-time tracking without the need for manual scanning. This enhances efficiency and accuracy across various operations.
- Another important aspect is high data storage capacity, as RFID tags can store more detailed information compared to barcodes, making them more useful for businesses that require extensive data management. Additionally, durability and longevity make RFID tags resistant to damage from water, dust, and rough handling, ensuring reliable performance in various environments.
- RFID also offers fast and accurate data capture, which minimizes human errors and speeds up operations, making it a preferred choice for inventory management and logistics. Lastly, its customizable and scalable nature allows businesses of all sizes to adapt RFID solutions according to their specific needs, whether for small-scale tracking or large-scale enterprise applications.

Challenges and Limitations of RFID Definition
- Despite its numerous advantages, RFID Definition does come with some challenges and limitations that businesses should consider before implementation. One of the primary concerns is the high initial cost, as the price of RFID tags, readers, and infrastructure can be expensive, making it a significant investment for businesses.
- Another challenge is interference issues, where radio waves can be affected by materials such as metal and liquids, leading to inconsistencies in data capture. Additionally, security risks are a concern, as data breaches and unauthorized access to RFID systems require businesses to implement strong security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Lastly, integration complexity can be a hurdle, as implementing RFID into an existing system requires careful planning and technical expertise, making the process time-consuming. While these challenges exist, businesses can overcome them with strategic planning and the right technological support.

Future of RFID Technology
- The future of RFID Definition is bright, with technological advancements making the system more reliable and efficient. One significant trend is its integration with IoT (Internet of Things), where RFID is increasingly being used alongside IoT devices to enable real-time tracking and smart automation. This combination enhances efficiency across various industries.
- Another key development is blockchain for secure transactions, which ensures secure and transparent data exchange in RFID systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses can strengthen data security and reduce fraud risks. Additionally, AI-driven analytics is being incorporated into RFID to provide predictive insights and enhance decision-making, allowing companies to optimize operations effectively.
- Lastly, the expanded use of RFID in retail and healthcare is set to grow, helping businesses track inventory more accurately, improve security measures, and enhance overall operational efficiency. As these advancements continue, RFID Definition will play an increasingly vital role in various sectors.

How RFID Enhances Security and Authentication
- Security is a top priority for businesses, and RFID Definition plays a crucial role in enhancing security and authentication in various ways. One key application is access control, where RFID-based security systems restrict unauthorized access to high-security areas, buildings, and facilities. This ensures that only authorized personnel can enter designated spaces. Additionally, RFID enhances asset tracking, preventing theft and loss by maintaining a real-time log of valuable assets and equipment.
- Another important aspect is secure payments, as contactless RFID payments are widely used in banking and retail. These transactions are not only fast but also provide a secure way to process payments, reducing fraud risks. Lastly, personal authentication benefits from RFID-enabled biometric verification, which strengthens identity security for businesses and government institutions. This advanced level of authentication ensures that sensitive data and facilities remain protected from unauthorized access.

Benefits of RFID
RFID technology. offers several benefits across various industries. One of its key advantages is improved inventory management, as it allows businesses to track inventory in real-time, reducing errors and enhancing stock accuracy. This minimizes overstocking and stockouts, leading to better supply chain efficiency. Additionally, RFID provides faster and contactless data capture since, unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require a direct line of sight to be scanned. This significantly speeds up processes in warehouses, retail stores, and logistics operations.
Another major advantage is enhanced security and anti-theft measures. RFID is widely used in access control and theft prevention, helping track valuable assets and prevent unauthorized access. Moreover, RFID contributes to automation and reduced labor costs by eliminating the need for manual data entry, thereby cutting labor expenses and reducing human errors.
In retail, RFID plays a crucial role in delivering a better customer experience by enabling faster checkouts, ensuring accurate product availability, and creating seamless shopping experiences. It also supports personalized marketing by tracking customer preferences. Furthermore, RFID enhances supply chain visibility by providing real-time tracking of goods, improving efficiency in logistics, shipping, and distribution.
Lastly, RFID tags offer durability and reusability, making them a cost-effective solution in the long run. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags are more robust and can be reused multiple times, further enhancing their value in business operations.

Best Practices for Implementing RFID in Business
- Assess Business Needs – Understand the specific requirements and goals before implementing RFID.
- Choose the Right RFID Type – Select passive or active RFID tags based on the intended application.
- Ensure System Compatibility – Integrate RFID with existing inventory and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- Train Employees – Educate staff on RFID technology to prevent errors and maximize efficiency.
- Monitor & Optimize – Continuously analyze RFID data to improve tracking accuracy and security.
Conclusion: Is RFID Right for Your Business?
RFID Definition offers businesses a smarter way to manage operations by improving accuracy, reducing manual work, and enhancing security. While the initial setup may seem costly or complex, the long-term benefits — like real-time tracking, better inventory control, and smooth automation — make RFID a smart investment. From retail and logistics to healthcare and security, RFID is changing how industries operate.
As technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain continue to grow, RFID systems will become even more powerful. The future of RFID is not only about tracking but also about smarter decision-making and increased efficiency.
AIDC Technologies India: Simplifying RFID for Your Business
AIDC Technologies India provides complete RFID solutions that are tailored to your business needs. Whether you need RFID tags, readers, or system integration, AIDC ensures smooth implementation and support. With a focus on reliability, security, and ease of use, AIDC helps your business move forward with confidence.
FAQs
1. What is RFID used for in business?
RFID is used to track items, control inventory, and improve security in real time.2. Can RFID replace barcodes completely?
RFID can do more than barcodes, but both can work together depending on business needs.3. Is RFID expensive to install?
Initial costs can be high, but long-term savings and efficiency make it worthwhile.
4. Where is RFID used the most?
Industries like retail, logistics, healthcare, and security use RFID the most.
5. How long do RFID tags last?
Passive RFID tags can last for years, while active tags last based on battery life.
Let AIDC Technologies India help you automate and secure your business. Connect with our team today and upgrade your operations with RFID.